STERiGLIDE™ In-Depth
Needle vs. Microcannula
STERiGLIDE™ In-Depth
Needle vs. Microcannula
Until recently the only, and preferred, method for delivery of soft tissue fillers, such as collagen, hyaluronic acid, or autologous fat, to the face and hands has been via a sharp tipped hypodermic needle. However, recent advancements in the production of blunt tipped cannulas, and more specifically micro-cannulas, has set the cat amongst the pigeons and changed this landscape, forever.
Options including STERiGLIDE™ from TSK Laboratories provide the next generation in micro-cannulas for the cosmetic sector. Both clinical practitioners and patients are embracing the benefits that blunt micro-cannulas have over their sharper cousins – marking them out as a true ‘game-changer’.
Needle flexibility and control
While sharp tipped needles are rigid in nature, cannulas are a more flexible option as this means that they can move more freely and easily when delivering precise aesthetic enhancements. To overcome this, the STERiGLIDE™ micro-cannulas offer a solution which is more rigid than many other cannula products, yet still more flexible than a needle – this allows practitioners to control their movements in a more predictable, yet flexible fashion.
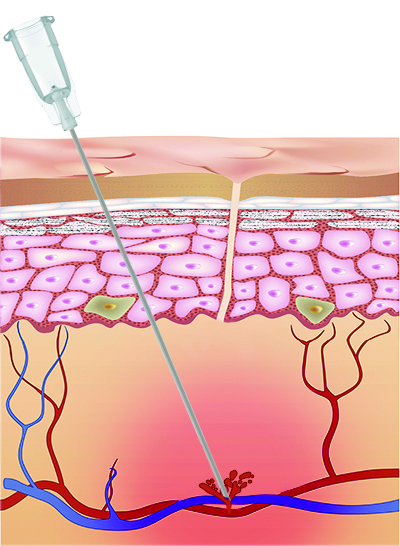
Using sharp needle
Cross-section of dermal layer using a sharp need.
Using STERiGLIDE™ microcannula
Section of the dermal / Filler injection with cannula
Number of entry points
Sharp needles require multiple entry points to deposit the chosen product in a bolus or linear fashion across a given area. Cannulas can be used through fewer entry points to deposit filler in a fan-like or matrix pattern. This is because they can be pushed through the tissue freely and easily, without cutting. This makes treatment quicker and less painful, without repeated needle entry. Similarly, it causes less swelling and bruising thanks to the reduction in tissue subcision. For treatments in more sensitive areas, such as the tear trough, there are many who note that using blunt tipped micro-cannulas is the ONLY sensible option.
Patient comfort and down-time
In a competitive marketplace, where patients are demanding less downtime, the need to deliver more comfortable and less traumatic treatments becomes imperative for practitioners. One clinical study by American Plastic Surgeon, Sam Sukkar M.D. sought to compare the swelling, pain and bruising experienced with a blunt tipped microcannula and a sharp tipped needle for the injection of dermal filler into naso-labial folds.
The study of 11 patients concluded that blunt tipped micro-cannulas showed more rapid patient recovery than sharp tipped needles. Pain scales scored at the point of injection were slightly less with the cannula, and swelling was significantly reduced compared to the use of a sharp needle.
Different types of cannulas
When thinking about investing in blunt tipped micro-cannulas for your cosmetic practice, it’s important to realize that they are not all the same.
There are many aspects to consider which will affect the reliability of the device itself and optimum product placement. From the position of the side port, through which product is extruded, to the shape of the tip, the thinness of the cannula walls, and its external composition which will affect the free movement of the cannula; there is much to take into account.
Two types of micro-cannulas
TSK Laboratory offers two distinct types of micro-cannula to the aesthetic marketplace. The traditional CSH (Closed-tip Side Hole) micro-cannula range comes with a round-shaped tip and features ultra-thin walls.
TSK’s flagship STERiGLIDE™ range of ultra-thin walled micro-cannulas introduced a domed or tapered shape to its blunt tip. This newly designed tip provides less resistance on cannula entry than a traditional round tip, which in turn reduces friction through the tissue, reduces the force need to introduce the cannula, and minimal bruising for the patient. Combined with a more rigid construction and a proprietary surface treatment to the stainless steel of the shaft, STERiGLIDE™ has a 50% improvement in its ability to glide through the structures.
Its side port, the orientation of which is visibly marked on the hub, is also located as near to the tip as possible for accurate product delivery and minimal product loss.
All of these design features have made STERiGLIDE™ a cut above traditional micro-cannulas, award-winning and considered by many as the gold standard for blunt-tipped micro-cannulas for use in aesthetic practice.

The #1 Choice
STERiGLIDE™ is the gold standard for microcannula -Outperforming any other available
Created by TSKLab
The #1 Choice
STERiGLIDE™ is the gold standard for microcannula -Outperforming any other available
Created by TSKLab
What sets STERiGLIDE™ apart from the rest?
Dome shaped tip design
Easier cannula introduction
Reduced risk of bruising
The patented dome shaped tip of the STERiGLIDE™ offers less resistance than a traditional cannula tip. This reduces the cannula introduction force needed and the risk of bruising.
Nearest to tip filler delivery
More accurate filler placement
Reduced product loss
Practitioners can see and feel the end of the cannula tip. Delivery of filler near the end of the tip creates a more accurate sense of filler placement. It also reduces product loss at the distal end of the tip.
Proprietary surface treatment
Up to 50% better gliding
Increased patient comfort
STERiGLIDE™ cannulas are made of the highest quality steel with a proprietary surface treatment coating. This reduces friction within the soft tissue enhancing patient comfort. The surface treatment also improves the handling and maneuverability of the cannula.
Clear side-port marking
More accurate filler placement
Better handling
The hard polymer hub of the STERiGLIDE™ cannula has a clear side-port marking that indicates the position of the cannula opening while serving as a visual guide for more accurate filler delivery.